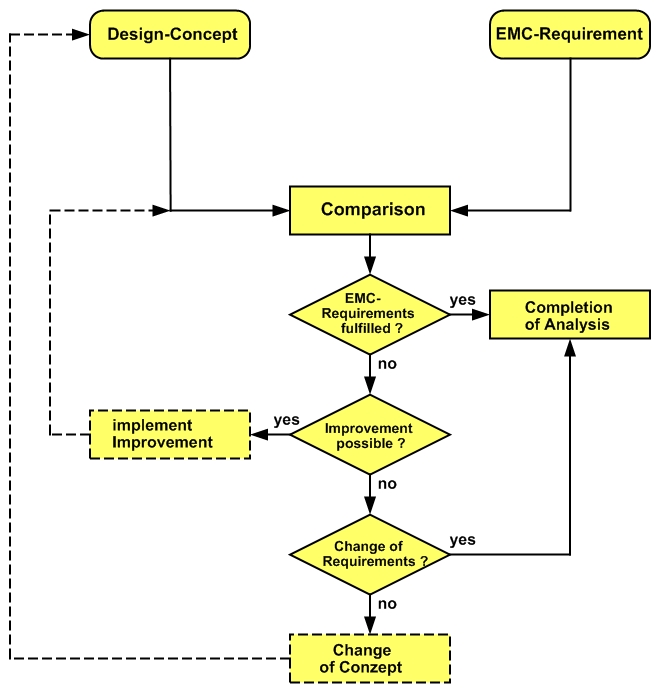
General Scheme of EMC Analysis
EMC-Analysis
The purpose of the EMC analysis is to provide information already in the planning phase, whether the intended design concept makes it possible or probable to meet the EMC requirements - and thus to identify necessary corrections at a very early stage of development.
Performing the EMC analysis means the line-up and comparison of
Device properties versus requirements regarding noise emission
(Noise sources inside the device ==> coupling, noise level)
Device properties versus immunity requirements
(Disturbance variables, coupling ==> noise victims, noise thresholds in the device)
This procedure can be used not only for the planning of new devices, but also for the analysis of existing systems - if e.g. the measurement results do not meet expectations.
By means of an EMC analysis, the theoretically possible results can be obtained using Simulations. Conclusions can be drawn from the comparison with the real measurement results - at which points deviations are present, what is the cause and what measures are to be taken.
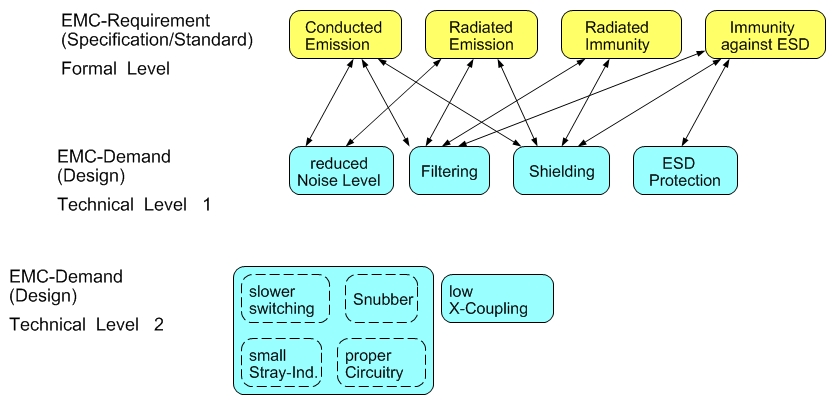
Formal EMC-Requirement Technical EMC-Demand
The figure compares the EMC-Requirements from specifications and standards, the formal level, with the EMC-Demands on the part of the device design, the technical level.
It can be seen that a single EMC requirement, such as the noise emission at the artificial network (LISN), does not have a single equivalent on the technical side, but several: in addition to the filtering of the noise, is also addressed a reduction of the generated noise level and a shielding to prevent the coupling or radiation of the noise.
Conversely, technical features such as e.g. filtering, are influencing a whole range of EMC requirements (emission via lines and via antenna and immunity to radiation and ESD, etc.)
The technical EMC-Demands can be further broken down - e.g. for the reduction of the generated noise level: slower switching, small stray inductivities on switching converters, the use of snubbers etc.
This results in a somewhat extended flow chart for the EMC analysis
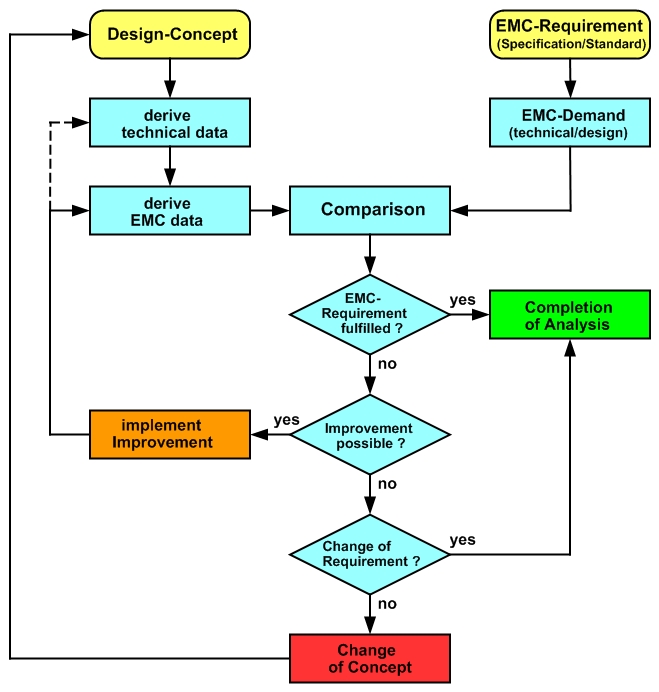
Extended Flow-Chart of EMC-Analysis
In the extended EMC analysis not only the formal EMC requirements are considered, but also the design-technical demands, which are necessary to achieve this formal EMC requirement.
In the flow chart, the way of changing the concept is colored in red to highlight the potentially particularly negative impact on projects when necessary design changes are detected at a relatively late time (e.g., first in the B or C sample).
All the more important are Simulations with which the design concept can be checked at an early stage - and corrected if necessary.
© Ingenieurbüro Lindenberger 8447

